





Chipmunks
Chipmunk Facts
Chipmunks are small, ground-dwelling members of the squirrel (Sciuridae) family known for their burrowing habits and love of nuts. Despite their size, chipmunks can cause significant damage to homes, yards, and farms. Below, learn important information about chipmunks, including general facts and how to identify chipmunk damage.

General Chipmunk Facts
- Chipmunk Classification - Genera:
- Tamias (eastern chipmunk - sp. Tamias striatus)
- Neotamias (mostly western chipmunks - 23 existing species)
- Eutamias (Siberian chipmunk - sp. Eutamias sibiricus)
- Average Size: 2-6" long with a 3" tail; less than 1 lb. in weight
- Average Lifespan in the Wild: 2-3 years
- Identifying Features: Shades of brown/yellow/grey fur with white and black stripes down the back
Chipmunk Geography
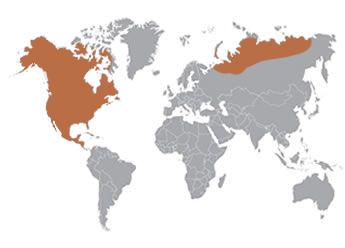
All species of chipmunks are native to North America, except one - the Siberian chipmunk. As indicated by its name, the eastern chipmunk inhabits most of the eastern half of the United States and Canada. Western chipmunks inhabit the western states as well as most of Canada.
The Siberian chipmunk is the only species that is found outside of North America - its range extends throughout northern Asia, from central Russia to Japan.
Chipmunk Habitat

Chipmunks feel most at home in areas with plenty of ground cover, including logs, trees, stumps, shrubs and rocks. While the ideal habitat for chipmunks is a deciduous forest, woodland or brushland, they’re also comfortable in other areas that provide sufficient cover such as urban parks, fence lines, hedges and houses.
Chipmunks dig extensive burrow systems directly underneath or next to natural or manmade cover. They dig two types of burrows: shallow burrows in which they seek refuge while foraging during the day, and deeper, more complex burrows where they nest, store food and spend most of the winter months. Chipmunks rarely venture further than 1/3 mile from their burrows at any time.
Chipmunk Diet
Chipmunks are omnivores, dining on various types of foods that are found mostly on the ground. Their diets are more diverse during the warmer months, during which time they hoard nuts and seeds in their burrows to eat in the winter.
Some favorite foods include:

Chipmunk Behavior
- Activity: Chipmunks are active in the daytime during spring, summer and fall. Chipmunks remain in their deep burrow systems during the winter, where they enter patterns of torpor (deep sleep and lower body temperature) interrupted by periods of feeding.
- Reproduction: Breeding occurs twice per year - once in the spring and once in the summer - when chipmunks give birth to 4-5 babies at a time.
- Burrowing: Chipmunks dig their own pairs of burrows, excavating as deep as 3 feet underground. Burrows are typically dug directly underneath or next to cover, because a chipmunk always requires protection from predators. Oftentimes chipmunk burrows cause damage when dug next to a home foundation
- Hoarding: To prepare for the winter hibernation period, chipmunks begin to stockpile nuts and seeds in their burrows during late summer and early fall.
- Communication: Chipmunks are protective of their burrows and use a range of loud chirps as well as body language to express occupied territory, dominance, or warn their young of danger. Females also have a mating call for which they use their high-pitched, bird-like vocalizations.
Identify Chipmunk Damage

Though chipmunks are small, they can be quite destructive - especially when burrowing near a home's foundation.
Here are some signs of chipmunk damage:
- structural or foundational damage from chipmunk burrows
- holes in lawn or garden from digging for plant roots
- seed piles underneath bird feeders
- uprooted bulbs
- chipmunk tracks: tiny prints with four toes in the front and five in the back (front and hind feet are generally reversed)
Fun Facts
- One tiny chipmunk can gather up to 165 acorns in one day.
- Chipmunks have pouches inside of their cheeks in which they store food when foraging.
- The main entrance of a chipmunk burrow can extend up to 20 feet in length.
- A group of chipmunks is called a scurry.
